NR 5G RRC Overview
The Radio Resource Control (RRC) state machine for New Radio (NR) is shown in Fig. 4.2.1.1A UE starts from RRC Idle mode when it first camps on a 5G cell. for example. This can happen immediately after the device is switched on, or it can happen after inter-system cell reselection from LTE. A UE makes the transition from RRC idle to RRC Connected by completing the RRC setup process. An RRC connection is a logical connection between the UE and the base station.
In RRC connected mode a UE is assigned one or two C-RNTI (Cell Radio Network Temporary Identifiers). C-RNTI is used for addressing UEs when it require resource allocation from cell. A single C-RNTI is allocated when the UE is connected to a single base station. Two C-RNTIs are allocated when UE is connected using Multi-RAT Dual Connectivity (MR-DC)
In RRC connected mode a UE is configured with at least one Signaling Radio Bearer (SRB) and usually one or more Data Radio Bearers (DRB). SRBs can be used to transfer signaling messages between the UE and the base station. Signaling messages can be related to the RRC signaling protocol or the non-access striatum (NAS) signaling protocol. The base station uses the NG Application Protocol (NGAP) to transfer NAS messages to and from the AMF. The DRB can be used to transfer application data between the UE and the base station. Base station Uses a GTP-U tunnel to transfer data to and from the UPF.
UE has to change to RRC connected mode to register with the network, i.e. to change from RM-deregistered to RM-registered. Once a UE is registered with the network the UE will normally remain RM-registered, regardless of the RRC state. The registration process allots the UE with a temporary identity known as 5G-S-TMSI. Use of temporary identification instead of permanent identity, e.g. IMSI helps to improve security.
UE has to change to CM-IDLE to CM-connected, the UE must change to RRC connected mode. UE is returned to the CM-IDLE Whenever a RRC connection is released. The UE remains in CM-connected until change it state from RRC Connected to RRC idle.
A UE change from RRC Connected to RRC Inactive using the RRC Release procedure. The RRC release message includes a 'suspendConfig' parameter structure that indicates that the UE is being moved to RRC inactive instead of RRC idle. The NG signaling connection between the base station and the AMF is maintained while the UE RRC is inactive. In addition, GTP-U tunnels are maintained between the base station and UPF (one GTP-U tunnel per PDU session). UE context is also maintained by both the network and the UE
The RRC Idle state allows the UE to return to RRC Connected and begin transferring application data or signaling messages with minimal latency. For RRC-associated signaling load is reduced relative to inactive RRCs because the UE context is already established. The RRC idle state allows the UE to reduce the battery power consumption associated with the RRC. This can be achieved with longer DRX cycles and does not require channel quality reporting.
A UE change from RRC Connected to RRC Inactive using the RRC Release procedure. The RRC release message includes a 'suspendConfig' parameter structure that indicates that the UE is being moved to RRC inactive instead of RRC idle. The NG signaling connection between the base station and the AMF is maintained while the UE RRC is inactive. In addition, GTP-U tunnels are maintained between the base station and UPF (one GTP-U tunnel per PDU session). UE context is also maintained by both the network and the UE
The RRC Idle state allows the UE to return to RRC Connected and begin transferring application data or signaling messages with minimal latency. For RRC-associated signaling load is reduced relative to inactive RRCs because the UE context is already established. The RRC idle state allows the UE to reduce the battery power consumption associated with the RRC. This can be achieved with longer DRX cycles and does not require channel quality reporting.
The AMF can request the base station to provide notifications when the UE moves between RRC connected and RRC inactive. This request can be included in the ngap 'Initial context setup request' or 'UE context modification request' messages. The base station subsequently provides updates using the NGAP 'RRC inactive Transition Report'. The AMF can use this information to adjust its observation timer with respect to the RRC status of the UE. For example, if the AMF knows that the UE is connected to the RRC it can expect a rapid response to any downlink transaction and therefore it can implement a relatively short supervision timer. If the AMF knows that the UE RRC is inactive it can expect a less rapid response to any downlink transactions as those transactions must be paginated in the UE before forwarding to the UE. The amf can thus apply a long observation timer to the UE that is RRC inactive.
Switching between NR RRC CONNECTED <-> INACTIVE <-> IDLE State Change
UE is in CM-CONNECTED state
UE stores Access Stratum context
UE reads System Information
UE monitors the Paging by PDCCH DCI using the P-RNTI
UE is addressed using C-RNTI allocated by gNodeb
Connected Mode DRX can be configured
Mobility is based upon handovers
AMF maintains NG signalling connection with gNodeb
UPF maintains GTP-U tunnels with gNodeb
Radio Access Network is responsible for UE reachability
Uplink and downlink data can be transferred
UE reports Channel State Information (CSI)
UE monitors Control Channels for Resource Allocations
UEs supporting CA, use of one or more SCells, aggregated with the SpCell, for increased bandwidth
UEs supporting DC, use of one SCG, aggregated with the MCG, for increased bandwidth
RRC CONNECTED
UE stores Access Stratum context
UE reads System Information
UE monitors the Paging by PDCCH DCI using the P-RNTI
UE is addressed using C-RNTI allocated by gNodeb
Connected Mode DRX can be configured
Mobility is based upon handovers
AMF maintains NG signalling connection with gNodeb
UPF maintains GTP-U tunnels with gNodeb
Radio Access Network is responsible for UE reachability
Uplink and downlink data can be transferred
UE reports Channel State Information (CSI)
UE monitors Control Channels for Resource Allocations
UEs supporting CA, use of one or more SCells, aggregated with the SpCell, for increased bandwidth
UEs supporting DC, use of one SCG, aggregated with the MCG, for increased bandwidth
RRC INACTIVE
UE stores Access Stratum context
UE reads System Information
UE monitors the Paging by PDCCH DCI using the P-RNTI
UE monitors the PCCH for CN paging using the 5G-S-TMSI and RAN paging using the I-RNTI
UE applies DRX for paging
Mobility is based upon Cell Reselection
AMF maintains NG signalling connection with gNodeb
UPF maintains GTP-U tunnels with gNodeb
Radio Access Network is responsible for UE reachability
UE Performs RNA updates
gNodeb knows the UE location with a resolution of a RAN Notification Area (RNA)
<Table 1.>
<Table 2.>
<Table 3.>
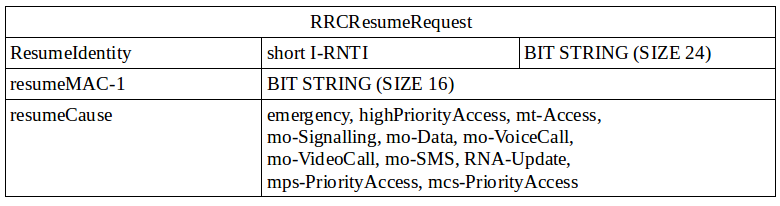
Signalling used to resume an RRC Connection at a Target eNodeb
Figure 112. shows the signaling call flow used to resume the RRC connection at a Target gNodeb. UE initiates the process by sending either RRC Resume Request or RRC Resume Request 1. The contents of these messages are presented in Tables No. 2 or 3. The selection is based on the 'useFullResumeID' flag present in SIB1. Both messages contain I-RNTI, MAC-I and cause values. The MAC-I information element is used to authenticate the UE before the UE is re-enter to RRC Connected at source gNodeb.<Figure 112>
RRC IDLE
UE is in CM-IDLE stateUE reads System Information
UE monitors the Paging by PDCCH DCI using the P-RNTI
UE monitors the PCCH for CN paging using the 5G-S-TMSI
UE applies DRX for paging
Mobility is based upon Cell Reselection
Core Network knows UE location with resolution of Registration Area (one or more Tracking Areas)
UE performs Registration Area updates with Core Network
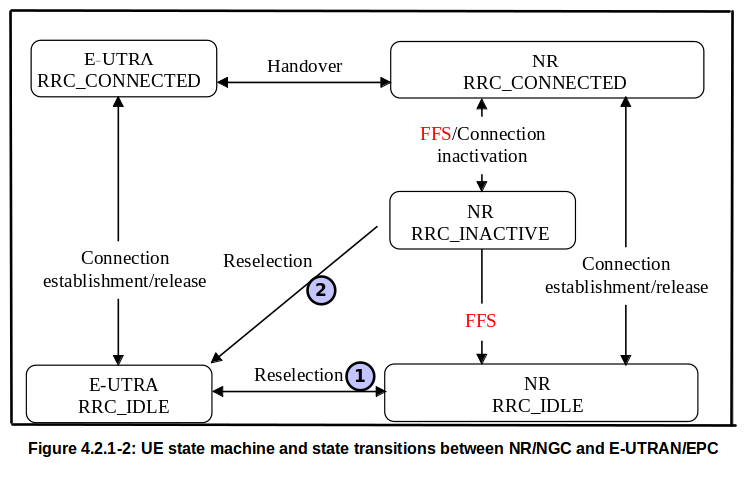
NR RRC Interaction with LTE RRC
NR RRC is involved not only in NR but also in other radio access technology. The interaction of NR RRC and LTE RRC can be represented as follows. Here are the things to note1. when UE in idle state it's NR RRC IDLE can reselect to EUTRA RRC IDLE and EUTRA RRC IDLE can reselct to NR RRC IDLE.
2. But, when UE is in NR RRC INACTIVE state, it can select to EUTRA RRC IDLE state, but EUTRA RRC IDLE state cannot reselect to NR RRC INACTIVE state.