Q1. What is MIMO and what are the functionalities of MIMO?
- (MIMO) stands for Multiple Input Multiple Output.
- The functionalities of MIMO it have multiple antenna at the transmitter side and multiple antenna also have at the receiver side.
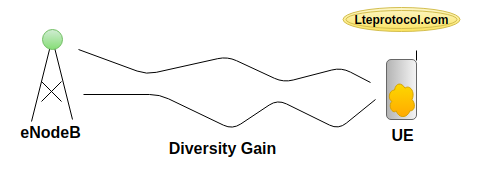
Q2. What is diversity and why it use in MIMO?
- Diversity is using to improve the reliability of the system.
- In diversity sender sends the data at different propagation (different paths).
- In MIMO we need the reliability or high speed data transmission so that we use two technique here 1. Spatial Diversity 2. Spatial Multiplexing.
Q3. What is Spatial Diversity?
- Spatial diversity is one of the fundamental benefits of MIMO technology.
- In short, diversity aims to improve the reliability of the system by sending same data over different propagation, or spatial, paths.
Q4. What is Spatial Multiplexing in MIMO?
- Spatial Multiplexing (SM, SMX) also known as Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) used to transmit data into independent channels separated by space.
- It’s like a pipeline through which data is flowing between the base station and the phone on a mobile network.
- Imagine a situation with one antenna on the base station and one on the phone that allows so much data to flow.
- Now, by installing more antennas on base station side with proper spatial separation, multiple virtual pipelines can be created in the space between phone and the base station.
- This creates multiple paths for more data to travel between the base station and mobile.
Q5. What are the advantages of MIMO?
- In MIMO UE experiencing good coverage (with high signal to noise ratios) can take advantage of the spatial multiplexing gain and can receive multiple parallel streams of data.
- Transmit and receive antenna have maximum number of parallel streams For example, 2x2 MIMO, 4x2 MIMO and 2x4 MIMO arc all capable of transferring a maximum of 2 parallel streams of data.
- UE in poor coverage (with a low signal to noise ratios) can take advantage of the diversity gain to help improve their signal to noise ratio.
- The magnitude of the diversity gain is dependent upon the number of receive antenna and the level of correlation between each of the propagation paths, i.e. the gain is maximised for a large number of receive antenna and uncorrelated propagation paths.
- This dependency upon channel conditions means that MIMO is used to transfer multiple parallel streams of data in good coverage conditions to maximise throughput, and is used to transfer a single stream of data in poor coverage conditions to maximise the diversity gain.
Q6. What are the disadvantages of MIMO?
- The drawbacks of MIMO are its increased implementation complexity and increased hardware requirement.
- MIMO requires additional processing at both the transmitter and receiver.
- It also requires additional signalling in terms of feedback from the receiver and resource allocation infonnation from the transmitter.
- MIMO requires additional power amplifiers at the transmitter side and additional receiving paths
- at the receiver side.
- lt also requires additional antenna elements at both the transmitter and receiver.
Q7. What is open loop? Why it use in MIMO?
- Open loop MIMO sender requires feedback from the receiver in terms of Rank Indication (RI) and Channel Quality Indicator (CQI).
- It’s called 'open loop' because of sender does not requiring feedback from transmitter in terms of a Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI).
- Open loop MIMO can be beneficial for high mobility scenarios which would cause a reported PMI to become invalid after only a short period of time
Q8. What is Close Loop in MIMO?
- In Closed loop MIMO sender require feedback from the receiver in terms of RI, CQI and PMI.
- The receiver selects a PMI to help improve the properties of the composite channel coefficient matrix.
- Closed loop MIMO allows senders to transmits with increased informations.
- But it also increased the signalling overhead.
Q9. What is diversity gain in MIMO?
- Diversity gain reduces the impact of fading when the fades on each propagation path are uncorrelated, i.e. one path may experience a fade while another path may not experience a fade.
- The receiver takes advantage of the paths which are not experiencing fades.
Q10. what is array gain in MIMO?
- Array gain is achieved from the beamforming effect which is generated when transmitting from multiple antenna elements.
- Beamforming directs the transmitted signal towards the UE and improves the received signal to noise ratio.
Q11. What is spatial multiplexing gain MIMO?
- Spatial multiplexing gain increases throughput by transferring multiple streams of data in parallel using the same set of time and frequency domain resources.
- Uncorrelated transmission paths allow the receiver to differentiate between the data streams.
Q12. According to 3GPP release 15 is mimo support in uplink direction if yes the what’s are combination support of mimo have?
- The 3GPP release 15 version of the specifications for New Radio (NR) supports MIMO in both the uplink and downlink directions.
- The uplink supports 2x2 MIMO and 4x4 MIMO, whereas the downlink supports 2x2 MIMO. 4x4 MIMO and 8x8 MIMO.
- The release 15 version of the specifications also supports Multi-User MfMO in both the uplink and downlink directions.
Q13. What is Single-User MIMO?
- Single User MIMO allocates a different subset of PRB to each UE, i.e. the UE are separated in the frequency domain.
- The UE which are scheduled during a specific time slot do not need to be spatially separated and a relatively high MCS can be allocated, because the transmissions to each UE do not interfere with each other.
Q14. What is Multi-User MIMO?
- Multi-User MIMO takes advantage of beamforming to allocate the same set of time and frequency domain resources to multiple UE.
- These UE are separated in the spatial domain so they are able to re-use Physical Resource Blocks (PRB) without generating significant levels of interference towards each other.
Q15. What are the advantage of MU-MIMO?
- Increased Network Capacity – Network Capacity is defined as the total data volume that can be served to a user and the maximum number of users that can be served with certain level of expected service.
- Improved Coverage – With massive MIMO, users enjoy a more uniform experience across the network, even at the cell’s edge, so users can expect high data rate service almost everywhere.
- User experience – Ultimately, the above two benefits result in a better overall user experience users can transfer large data files or download movies, or use data-hungry apps on the go,













0 comments:
Post a Comment
Dear reader if you have any question that's you want to know answer please write it to in comment box i will post answer ASAP..!!