Q21. How many SIBs are using in LTE? Explain?
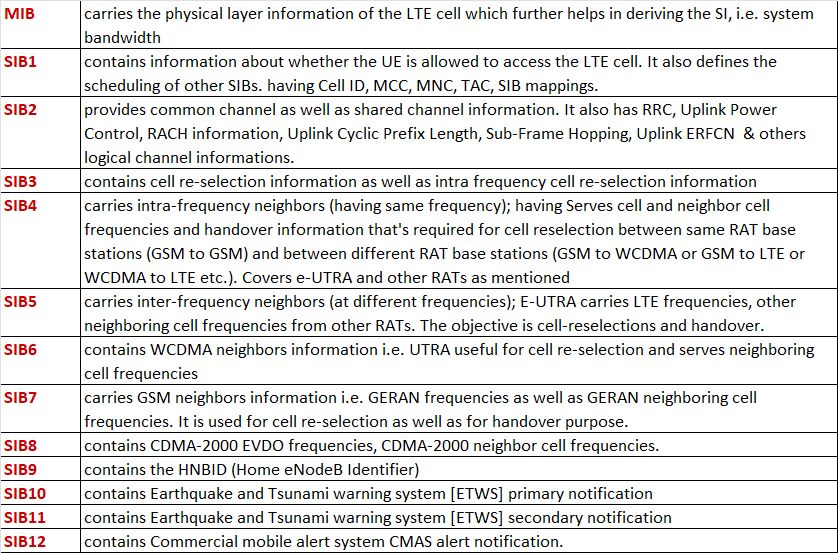
Q22. What are the information presents in SIB2 & SIB3?
Ans. In LTE, SIB2 and SIB3 are two important system information blocks (SIBs) that are broadcasted periodically by the network to provide essential information to the mobile devices.
The information present in SIB2 includes:
Radio Resource Config Common Information
Access Class Barring Information
UE Timers And Constraint Information
Time Alignment Timer Common Information
The information present in SIB3 includes:
Cell Reselection Info Common
Cell Reselection Serving Frequency Info
Intra Frequency Cell Reselection Info
Q23. Which SIB UE will get the information of random access procedure (RAP)?
Ans. In LTE, the system information block (SIB) that contains information related to the Random Access Procedure (RAP) is SIB2.
SIB2 provides important configuration parameters for the UE to initiate and complete the random access procedure, including the preamble format, the RA response window size, the contention resolution timer, the backoff indicator, and other relevant parameters.
Once the UE has received SIB2, it can use the information to perform the random access procedure and request access to the network.
Q24. Why be need for the RACH procedure in lte and PRACH?
Ans. The RACH procedure is typically used by a UE when it needs to establish a new connection with the network, such as when it first powers on or when it enters a new coverage area. The UE sends a random access preamble on the Physical Random Access CHannel (PRACH) to the network, which triggers a series of exchanges to establish a connection.
The need for the RACH procedure arises from the fact that LTE networks are designed to support high-speed data services, which require efficient and reliable resource allocation. By using the RACH procedure, the network can allocate resources to the UE in a controlled and efficient manner, based on the UE's access request and the network's capacity.
The PRACH, which is a dedicated uplink channel used for the RACH procedure, provides a reliable and robust mechanism for the UE to transmit its access request to the network, even in cases where the UE's signal strength is low or the network is heavily loaded.
Q25. What are the difference between RACH and SCHEDULING REQUEST?
Ans. The RACH procedure and the Scheduling Request (SR) mechanism are both used in LTE for uplink resource allocation, but they serve different purposes and have different characteristics. Here are the main differences:
Purpose:
RACH is used by a UE to initiate an Access request and transmit initial control information, such as measurement reports or uplink data packets, while SR is used by a UE to request uplink resources for transmitting scheduled data.
Channel:
RACH uses the Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH), which is a dedicated uplink channel used exclusively for the RACH procedure, while SR uses the Physical Uplink Control Channel (PUCCH, PUSCH), which is a shared uplink channel used for both control as well as data transmissions.
Transmission Timing:
RACH is typically triggered by the UE when it needs to establish a new connection with the network, such as when it first powers on or when it enters a new coverage area, while SR is triggered by the UE when it has data to transmit and requires uplink resources.
Signaling Overhead:
RACH requires a longer transmission time and more signaling overhead than SR, as it involves multiple transmissions of the random access preamble and additional signaling exchanges to establish the connection, while SR involves a single transmission of a scheduling request message.
Resource Allocation:
RACH uses contention-based resource allocation, where the UE competes with other UEs for available resources on the PRACH, while SR uses semi-persistent resource allocation, where the network allocates dedicated resources to the UE for a period of time, based on the UE's request.


0 comments:
Post a Comment
Dear reader if you have any question that's you want to know answer please write it to in comment box i will post answer ASAP..!!