Q09. Explain the Interfaces uses in 5G NR Architecture?
Ans. The 5G System Architecture contains the following Interfaces:
N1: Interface between the UE and the AMF.
N2: Interface between the (R)AN and the AMF.
N3: Interface between the (R)AN and the UPF.
N4: Interface between the SMF and the UPF.
N5: Interface between the PCF and an AF.
N6: Interface between the UPF and a Data Network.
N7: Interface between the SMF and the PCF.
N8: Interface between the UDM and the AMF.
N9: Interface between two UPFs.
N10: Interface between the UDM and the SMF.
N11: Interface between the AMF and the SMF.
N12: Interface between AMF and AUSF.
N13: Interface between the UDM and Authentication Server function the AUSF.
N14: Interface between two AMFs.
N15: Interface between the PCF and the AMF in case of non-roaming scenario, PCF in the visited network and AMF in case of roaming scenario.
N16: Interface between two SMFs, (in roaming case between SMF in the visited network and the SMF in the home network).
N17: Interface between AMF and 5G-EIR.
N18: Interface between any NF and UDSF.
N22: Interface between AMF and NSSF.
N24: Interface between the PCF in the visited network and the PCF in the home network.
N27: Interface between NRF in the visited network and the NRF in the home network.
N31: Interface between the NSSF in the visited network and the NSSF in the home network.
Q10. What is gNB? And what’s the use of gNB in 5G NR?
Ans. the gNB logical architecture consists of a central unit
(CU) and distributed unit (DU), i.e., gNB=CU+DU. The CU controls the functioning of the DUs over the front-haul interface.
It is LTE Equivalent enhanced NodeB (eNB). The NR gNB supports connectivity to 5GC, and provides 5G-CP and 5G-UP protocol terminations towards the UE.
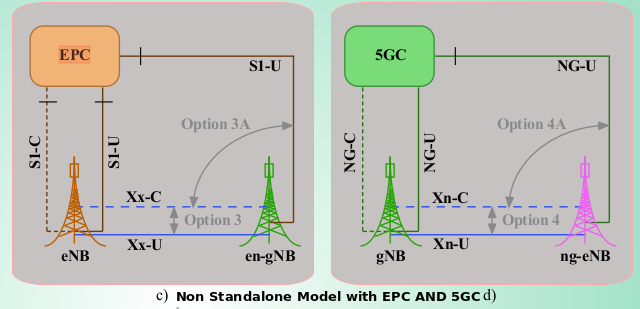
Q11. What is en-gNB? And How’s it different from gNB?
Ans. It is the node providing NR CP and UP protocol terminations towards their UE. The en-gNB is connected to the EPC via the S1 interfaces.
Q12. What is ng-eNB? And How’s it different from en-gnb?
Ans. It is the node providing E-UTRA CP and UP protocol terminations towards their UE. The ng-eNB is connected to the 5GC via the NG interfaces.
Q13. What is EPC and 5G NRC?
Ans. The EPC represents the Core of an LTE network. It is formed by multiple nodes, the main ones being MME, SGW, PGW and HSS. This nodes offer multiple functionality like mobility management, authentication, session management, setting up bearers and application of different Quality of Services.
5GC is the new 5G core network (5GC) defined by 3GPP. like previous generations, 5G deployment can use either the existing EPC or the 5GC. In addition, 5G introduced either in StandAlone mode (SA) using 5GC or in Non-StandAlone mode (NSA) with EPC/5GC, which find the best deployment in 5G.
Q14. What is NSA and SA? Name of the Deployment options available in NSA or SA as per 3gpp defined?
Q15. Explain frequency range define in 5G NR?
Ans. Frequency Range 1 (FR1) that includes sub-6GHz frequency bands.
Frequency Range 2 (FR2) that includes frequency bands from 24.25 GHz to 52.6 Ghz.
Q16. What is mmWave? Why it doesn’t it travels far from origin?
Ans. Millimeter waves, also known as extremely high frequency (EHF), is a band of radio frequencies that is well suited for 5G networks. Compared to the frequencies below 5 GHz previously used by mobile devices, millimeter wave technology allows transmission on frequencies between 30 GHz and 300 Ghz.
millimeter waves can travel recorded up to 10.8 kilometers at 14 spots that were within line of sight of the transmitter, and recorded them up to 10.6 kilometers away at 17 places where their receiver was shielded behind a hill or leafy grove.
Note: 5G signals can be blocked by physical barriers like walls and glass. Difficulty in moving found from outdoors to indoors that can be result, in poor coverage and slower download speeds.







0 comments:
Post a Comment
Dear reader if you have any question that's you want to know answer please write it to in comment box i will post answer ASAP..!!